what name is given to the crater at the top of a volcano caused by its collapse
ICSE Solutions for Course ix Geography – Volcanoes
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Exercises
I. Brusk Respond Questions.
Question 1.
What are known as volcanoes ?
Answer:
Volcanoes are the vents in the earth's crust erupting hot magma from the interior cadre motivated past endogenic forces.
Question two.
What is the difference between magma and lava ?
Respond:
Molten material moving under the globe's crust is called magma. When magma comes to the surface of the earth it is known as lava.
Question three.
Give one example each of an active volcano and a fallow volcano.
Answer:
- Active Volcano – Mt. Stromboli and Mt. Etna in Italy
- Dormant Volcano – Mt. Kilimanjaro of Africa.
Question 4.
What is the deviation between fallow volcano and an extinct volcano ?
Answer:
Fallow volcano can erupt at any interval merely extinct volcano tin can never erupt again.
Question 5.
What is the magma sleeping accommodation of a volcano ?
Reply:
The magma sleeping room is created by the molten magma itself past melting the surrounding rocks in the form of a huge chamber.
Question half-dozen.
Name two types of landforms made by volcanoes.
Respond:
Two types of landforms are :
- Extrusive landforms :
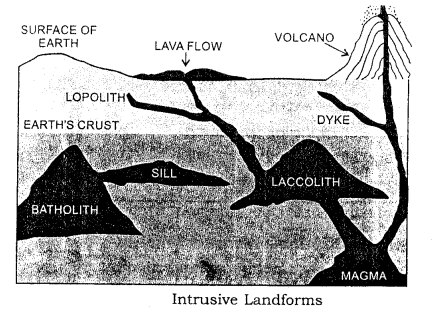
Extrusive landforms include crater composite cones caldere lava platforms. - Intrusive landforms :
Intrusive landforms include dykes batholiths laccoliths volcanic hill etc.
Question 7.
What is chosen the Pacific Ring of Fire ? Why is information technology called and then ?
Answer:
There are eighty% active volcanoes effectually the Pacific ocean which is called the Ring of Fire.
Question eight.
Name the three types of volcanoes on the basis of the frequency of their eruption.
Answer:
There are three types of volcanoes eastward.g. agile volcano which is still active in erupting magma dormant volcano which erupts in uncertain intervals and extinct volcano which has stopped eruption permanently it is also called dead volcano.
Question 9.
What are known equally Shield volcanoes ?
Answer:
A volcanoes erupting with plentiful lava spreading over the surface into several kilometres with huge circumference and taking a shape of shield are chosen as shield volcanoes.
Question 10.
Mention any two extrusive landforms caused by volcanic eruptions.
Reply:
- Blended cone : The volcano which erupts both lava and pyroclastic rocks form alternating layers of these 2 materials and build up to class composite cones. Examples : Fujiyama in Japan Vesuvius and Stromboli in Italy.
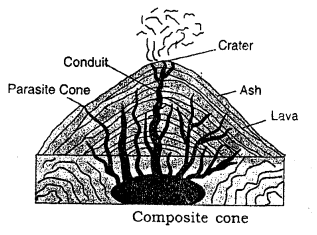
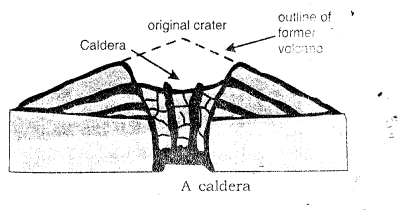
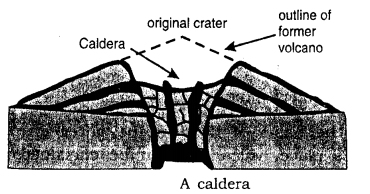
- Caldera : During repeated eruptions the tiptop of a valcano may be blown upward. In its place a large depression called caldera is formed. These are generally formed when the magma chamber is no longer able to emit sufficient magma and results in the plummet of a cone either partly or wholly.
Question 11.
Name any two intrusive landforms made by volcanic eruptions.
Answer:
- Batholiths : Large sized intrusions in igenous rocks. They occur at considerable depth and come to the surface in course of mount edifice activity.
- Laccolith : These are formed when magma spreads laterally in a dome shape. The dome also forces the overlying strata to bulge upward. The projecting landform is subjected to erosion and denudation. Thus laccolith comes to the surface.
Question 12.
How are hot springs formed ?
Answer:
The movement of magma heats upwards the underground water which converts into steam and gushes out through any crevice or holes on the crust.
Question 13.
What is chosen the Pacific Ring of Burn down ? Why is information technology chosen so ?
Answer:
There are 80% agile volcanoes around the Pacific bounding main which is chosen the Ring of Fire.
Question 14.
Give an case each of conical volcano and fissure volcano.
Answer:
Mountain Fuji in Japan is a conical volcano and Columbia plateau in South America and Deccan plateau in India are the examples of scissure volcanoes.
Question 15.
What is the difference betwixt dormant volcano and an extinct volcano ?
Reply:
Fallow volcano can erupt at any interval just extinct volcano can never erupt again.
2. Match the post-obit

Answer:

III. Fill in the blanks beneath
- The forces arising from the interior of the earth are called endogenic forces.
- The molten rock that reaches the surface of the globe is chosen magma.
- A lava shield is made upwardly of basic lava flows solidified away from the vent.
- Vents are intrusions of igneous rock that are vertical in shape.
- The Circum-Paciflc Chugalug is also chosen Pacific Ring of Burn.
4. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
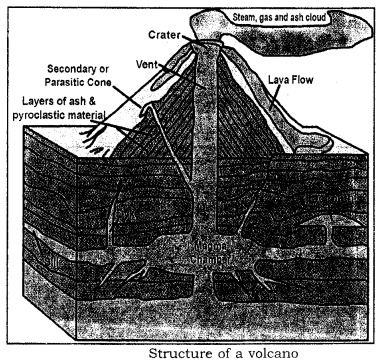
Explain the diverse parts of a volcano.
Answer:
A volcano represents some typical parts e.one thousand. the molten rock or magma mostly lava makes the conical trunk of a volcano. Magma bedroom is the source of erupting magma. Vent is the main channel through which the magma erupts outwards. Crater is the oral cavity or uppermost function of a volcano which is a large hole from which magma erupts and spreads all over.
Question ii.
Describe the causes of volcanic eruptions.
Respond:
The master causes of volcanic eruptions are the following :
- Heat and Pressure within the World : Temperature and pressure level both increase from the surface towards the centre of the world. Rocks are bad conductors of heat. And so the earth'due south heat does not escape on its own. Instead it melts the rocks and builds upwards great pressure. The pressure forces the heat to detect an escape route through fissures and cracks in the rocks.
- Plate Tectonics : Most volcanic eruptions take identify near plate margins. The same forces that cause earthquakes also cause volcanic eruptions.
- Magma Chamber : The molten material while still under the world's chaff melts weak rocks and creates a huge sleeping room for itself. Fresh magma continues to pour within the chamber. Since magma contains silicate materials gases and water vapours the pressure e'er acts vertically upwardly. Once a route is found it rises to the surface.
Question iii.
Explicate briefly the landforms created by volcanoes on the surface of the earth.
Answer:
The landforms created on world's surface are called Extrusive Landforms. These include volcanic plateaus volcanic mountains and volcanic plains.
(a) Volcanic Plateaus : These are derived from lava which flows from volcanic eruptions. The Plateau of Peninsular India particularly the north western Deccan is an example of lava plateau. Other examples are South African plateau Columbian Plateau and Ethiopian plateau.
(b) Volcanic Mountains : These mountains are built from material ejected from the fissures in the globe's chaff. Volcanic mountains are the well-nigh diverse because at that place are groovy differences in volcanic eruptions equally well as the materials they throw upwardly.
(c) Volcanic Plains : These plains are vast and smoothen formed by all-encompassing volcanic flooding from volcanic centres. The Western Victorian Plains in Victoria Australia are the finest examples of Volcanic Plains.
Question 4.
Write any iii destructive effects of volcanoes.
Answer:
Destructive Effects :
- When the volcanoes erupt they destroy life and holding. The hot lava together with ash and dust destroy non only human beings but too animals also as plant life.
- Agricultural fields are covered with layers of volcanic ash and dust making them unsuitable for cultivation.
- Huge clouds are formed after the eruption of volcanoes causing heavy rains which consequence in floods and landslides.
- Volcanoes too emit poisonous gases which pollute the surroundings and crusade health issues.
- Explosive volcanoes in ocean islands are followed 'by high Tsunami waves. They flood the area and destroy property people animals and crops.
Question v.
Describe the distribution of volcanoes in the world.
Respond:
Volcanoes are found along the weak zones of the earth's crust where due to continuous tussle by tectonic forces maximum active volcanoes have created. These are
- Cirum-Pacific Belt : It is also known as 'ring of burn down due to consisting 75 % agile volcanoes of the world.
- Mid-World Mountain Belt or Mid Continental Belt : It extends along the fold mountain zone of Alpine-Himalayan Region. Although this belt is noted for drastic convulsion simply these are some of the very destructive volcanoes e.1000. Stromboli Vesuvius Mt. Etna Mt. Pelee (West Indies). Out of these belts in that location are also various volcanoes scattered here and there.
Question half-dozen.
Describe of import volcanic landforms on earth.
Answer:
Prominent landforms associated with volcanoes are blended cones built of multiple material erupted out from a volcano. Conical hills are common in volcanic areas Crater lake is formed forth the mouth of a conical volcano which is filled with water afterwards cooling downwards of volcano. Due to repeated eruptions rima oris of a volcano is converted into a large depression called caldera. Lavashields are fabricated by big corporeality of bones lava flows making volcanic shields with a gentle slope.
Lava plateau : is formed by big calibration fissure eruptions covering extensive expanse e.g Columbia plateau in South America and Deccan plateau of Republic of india.
Practice Questions (Solved)
Question 1.
Name iii causes of volcanic eruptions.
Reply:
- Hot interior of the World
- Steam and gases
- Faults and fissures.
Question two.
Name the largest active volcano in the earth.
Answer:
Mauna Loa (Hawaii islands).
Question iii.
Which volcano is known as the 'light house of the Mediterranean ?
Answer:
Stromboli.
Question 4.
Name the three belts where volcanoes are found.
Answer:
- Circum Pacific belt
- Mid-world mount chugalug
- African rift valley.
Question v.
In which chugalug about of the volcanoes of the world are plant ?
Answer:
Circum Pacific Belt.
Question 6.
Name three causes of Earthquakes.
Answer:
- Volcanic eruptions
- Tectonic causes
- Elasticity of Rocks
Question 7.
What is epicentre ?
Answer:
The point on Earth'due south surface vertically in a higher place the focus is chosen epicentre.
Question 8.
Indicate the globe distribution of agile volcanoes.
Answer:
There are about 500 active volcanoes. Most of them are bars to Circum-Pacific Belt and Mid World Mountain Belt.
Question 9.
Give 2 reasons why tremors occur inside the earth?
Answer:
- Movements of the earth's crust forth lines of weakness produces groovy tremors.
- During volcanic activity movement of lava beneath the crust also causes tremors inside the globe.
Question 10.
Distinguish between :
- Seismology and Volcanology.
- Volcanic Grit and Volcanic Ash.
Reply:
- Seismology and Volcanology : Seismology is the science of study of earthquake and Volcanology is the science of study of volcanic phenomena.
- Volcanic Dust and Volcanic Ash : The finely pulverised fragments of rock are called volcanic ash and very fine particles which blow into air are chosen volcanic dust.
Question 11.
Draw the materials thrown out during volcanic eruption.
Respond:
The materials thrown out of a volcano due to eruptions are of three types :
- Solid materials :- The solid materials include large fragments of rocks known as volcanic Bombs. The finest particles include cinder volcanic ash dust.
- Liquid materials :- The liquid materials include basic lava and Acid lava. Acid lava has more silica while Basic lava has depression content of Silica.
- Gaseous materials :- The gaseous fabric is mainly composed of steam. The other gases include Oxygen Hydrogen Sulphuric acid Carbon dioxide etc.
Question 12.
Describe the effect of volcanic eruption of Karakatoa in 1883.
Answer:
Karakatoa island is situated betwixt the islands of Java and Sumatra in the Sunda strait. It suddenly erupted in 1883. The height of the mountain was blown away by the explosion xvi metres loftier tidal waves were caused killing 36,000 persons in west Java. Volcanic dust rose to a height of almost 27 kilometres. This dust encircled the globe for 3 years. Its consequence caused strange sunrise and dusk conditions.
Question 13.
Why is volcanic activity often associated with mountain edifice ?
Respond:
Most of the active volcanoes are formed along the fold mountains such as the Himalayas, The Alps, The Andes etc. Fold mountains have been formed by mount edifice movements. These involve intense folding and faulting which mark lines of weakness on the surface. Most of the eruptions take place along these lines of weak.
Question 14.
Draw the materials thrown out during volcanic eruptions.
Answer:
The materials thrown out of a volcano due to eruptions are of three types :
- Solid Materials : The solid materials include large fragments of rocks known as volcanic bombs. The finest particles include cinder volcanic ash and dust.
- Liquid Materials : The liquid materials include Basic lava and Acid lava. Acid lava has more of silica while Basic lava has low content of silica.
- Gaseous materials : The gaseous material is mainly composed of steam. The other gases include Oxygen Hydrogen Sulphuric acid Carbon dioxide etc.
Describe whatsoever three advantages of volcanoes.
- Many minerals from the interior of the Earth come up on to the surface.
- Fertile soils similar Black soil are made past breaking up of lava.
- Electricity is generated from gases emitted out during volcanic eruptions.
Question xv.
Why are Earthquakes related to volcanoes ?
Reply:
There is a close relationship between an Convulsion and a volcano Earthquakes and volcanoes occur in same belts i.due east. mid-world chugalug and Circum Pacific chugalug. Their distribution shows a similar pattern. Volcanic eruptions pb to Earthquakes. Volcanic eruptions are the local crusade of Earthquakes.
Question 16.
What is a geyser ? Give 2 of its main characteristics. Proper noun a well known geyser.
Answer:
Geyser : Geysers are fountains of super heated steam and hot water that is usually emitted with an explosion trigged off by gases escaping from below
Main Characteristics of Geysers
- H2o in a geyser gets heated up beyond its boiling point.
- They may spout to a height of over 150 feet.
A well known geyser is 'Quondam Faithful' in Xanthous Stone National Park of Wyoming. It erupts regularly every 60 minutes and attracts a large number of tourists.
Question 17.
State two ways in which lava may come out of the earth's crust giving an example of each type of these volcanic activities.
Answer:
Ii master types of volcanic eruptions are :
- Explosive and
- Serenity or Hawaiian.
- The Explosive eruption are the most tearing and destructive Explosion of pent up gases mainly steam cause enormous quantities of magma to be thrown into the air to form great clouds. Example Krakatoa volcano in Sunda Strait in Indonesia erupt in 1883.
- The Quiet eruption cause and other gases to escape. There is no vehement explosion. Lava flows the creaters and flows downwards the sides of the cone.
Instance : Hawaiian volcanoes and Maupa Loa.
Question 18.
(a) What do you understand by 'Vulcanism' ?
(b) What are 'Volcanoes' ?
(c) How are volcanoes formed ?
(d) Differentiate betwixt active dormant and extinct volcanoes.
(due east) What is'magma'?
(f) What exercise you lot understand by 'Crater of the Volcano' ?
Answer:
(a) The interior part of the earth is extremely hot temperature upto 2000°C. in which every matter converts into molten form. This molten textile 'magma' always tries to burst out whereever information technology finds any crack or pigsty in the crust. The procedure of erupting out of magma is known as 'vulcanism'.
(b) 'Volcanoes' are the outlets of magma through a vent or cracks in the form of a conical volcanic loma or through various holes known as crack eruption.
(c) Volcanoes are formed by the eruption of magma from the interior and deposited on the land surface and after cooling down take the shape of volcanoes.
(d) Active volcanoes become on erupting magma continuously e.g. stromboli (North of Sicily). Dormant volcanoes erupt in accidental intervals e.g. Mt. Vesuvius in Italy. Extinct volcanoes cease eruption for ever. e.g. Mt. Fujiyama in Japan.
(e) 'Magma' is the one give-and-take of several matters erupting out of a volcano eastward.g. lava, steam, cinderellas, stones, cinder, fume etc.
(f) Crater of a volcano is the mouth of volcano in its vertex in the form of a round pigsty.
Question 19.
(a) Depict the distribution of volcanoes in the world.
(b) What are the influences of volcanic eruptions on man ?
Respond:
(a) Volcanoes are found along the weak zones of the earth's crust where due to continuous tussle past tectonic forces maximum active volcanoes have created. These are :
- Cirum-Pacific Belt— It is besides known every bit 'band of burn due to consisting 75% active volcanoes of the globe.
- Mid-World Mountain Belt or Mid Continental Chugalug— Information technology extends along the fold mountain zone of Alpine-Himalayan Region. Although this belt is noted for drastic convulsion but these are some of the very subversive volcanoes due east.thou. Stromboli Vesuvius Mt. Etna Mt. Pelee (Westward Indies). Out of these belts there are also various volcanoes scattered hither and in that location.
(b) The furnishings of volcanoes on human life are both positive and negative :
Destructive influences :The deposition of lava makes the area very porous which creates water problem. The major flow of hot lava of Etna destroyed the whole area and property in Sicily. Mt. Vesuvius destroyed the urban center of Pompeii seven times since 79 AD. and the city of Herculaneum.
Constructive Influences :Volcanoes take provided some fertile lands due east.1000. Java and Deccan plateau and areas of S Brazil. Various precious minerals come out on the upper part of the earth'southward crust through eruption e.one thousand. Diamonds of Kimberley and gilded of Johannesburg in South Africa nickel deposits of Sudbury in Canada.
Question xx.
(a) What is an 'convulsion' ?
(b) Give ii major causes of earthquakes.
(c) Describe the world's distribution of earthquakes.
(d) Mention some of the main effects of earthquakes.
(e) Name the major earthquakes of India from 1991 to 1997.
Answer:
(a) An earthquake is tremor or convulsion of the earth's crust due to sudden movement of the crust.
(b) Two major causes of earthquakes are faulting associated with tectonic forces and the movements due to volcanic eruptions.
(c) The earthquakes are distributed along two major belts namely Circum Pacific earthquake chugalug (Ring of fire) and the Mid-World mountain earthquake belt along the great fold mountain zone.
(d) The destructive furnishings of earthquakes are very unsafe east.g. disruption of the rocks bed state slides changing the river courses floods tides collapsing of buildings destruction of transport lines and fires in electric wiring etc.
The constructive effects are the creation of additional coastal plains inlets trophy for skillful harbours creation of fissure- openings to class sulphur or hot springs etc.
(e) Major earthquakes of India from 1919 to 1997.
- Latur 1991
- Uttarkashi 1993
Question 21.
What are the post-obit
(a) Fissure type of volcanoes
(b) Spine or plug
(c) Caldera
(d) Mud volcanoes
(e) Epicentre
(f) 'Ring of Burn down'
(1000) Cinder Cone
Answer:
(a) Some times the volcanic eruption takes place through several modest holes which is known as scissure type volcanoes.
(b) The volcanic cone made past the quick solidification of pasty lava and having steep slopes is known as spine or plug.
(c) Caldera is the spacious crater of a volcano created past tremendous eruption. Crater lake in Oregon U.S.A occupies a caldera nigh 9 kilometre in diameter.
(d) Mud Volcanoes — A volcanic cone made of the mud due to the eruption of muddy water is called a mud volcano.
(e) Epicentre — Information technology is the place of surface position immediately higher up the origin or focus of an earthquake.
(f) 'Ring of Fire' — It is the chugalug around the pacific ocean where due to the weak crust 75% of active volcanoes exist forming a huge 'band of fire' phenomenon.
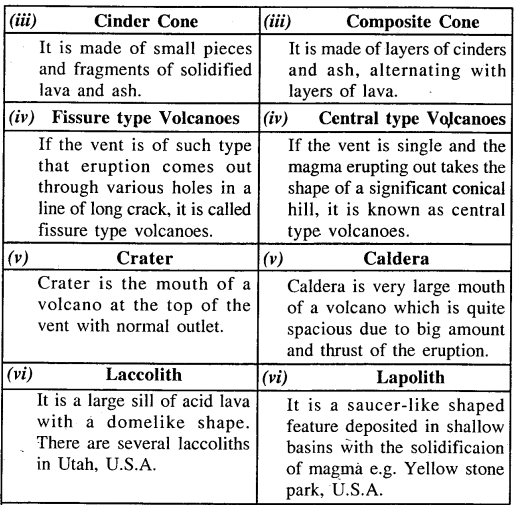
(g) Cinder Cone — The volcanic cone congenital of small-scale pieces and fragments of solidified lava and ash is chosen 'Cinder Cone'.
Question 22.
(a) Distinguish betwixt the post-obit pairs of terms associated with vulcanicity
- Lava and Magma
- Acidic Lava and Basic Lava
- Cinder Cone and Composite Cone
- Fissure-blazon Volcanoes and Central-types Volcanoes
- Crater and Caldera
- Laccolith and Lapolith
- Geysers and Hot Springs
(b) Distinguish between the post-obit pairs of terms associated with crustal movement of the earth
- Graben and Horst
- Tilted Block mountains and Lifted Block mountains
Answer:
(a)



Question 23.
Give a cursory account of 'Plate Tectonics'.
Answer:
In the beginning all the continents were combined together known as 'Pangasa' which afterward on splitted away and separated. Merely withal all continental and oceanic plates are sliding upon each other and result in various earthquakes and volcanoes. The continental drifting theory was discovered by German scientist Alfred Wagner in 1912 which supported this plate tectonics to prove the movement of the continental and oceanic plates working for changing the landforms of the crust.
Question 24.
Give reasons for the post-obit
- The Belts of volcanic activity and earthquakes are roughly the same.
- Basic lava cones are broader than Acid lava cones.
- The Circum-Pacific Chugalug of volcanoes is called 'The Ring of Burn down'.
Reply:
- The volcanoes and earthquakes are associated with each other as every volcanic activity takes place by shaking and breaking the weak crust which naturally creates tremors and earthquakes within the earth'southward crust.
- Bones lava cones are formed past liquid lava which expands and covers a large surface area while the Acid cones are formed by solid material e.thou. ash cinders etc which heap up but do not cover big expanse and form a high conical loma every bit compared to broad and low volcanic deposits on the surface.
- The circum-pacific belt is truly known as "The Belt of Fire" or "The Ring of Fire" as 75% active volcanoes erupting fire are located in this belt.
Question 25.
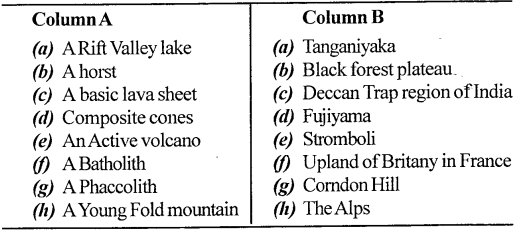
Match the items given in Cavalcade A with the right ones in Column B.
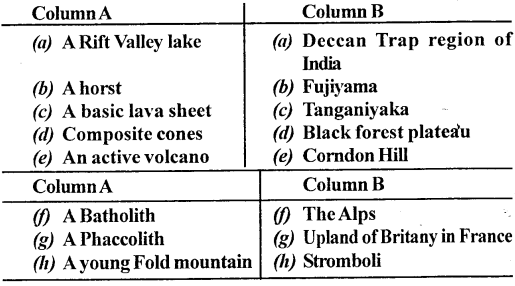
Respond:
Question 26.
Give one word for each of the following :
- A narrow block elevated between 2 normal faults.
- The funnel shaped hollow at the top of a volcanic cone.
- The lava which is poor in silica and rich in iron and magnesium.
- A volcano which has the possibility of erupting in future.
- A big sill of acid lava which has solidified gradually giving a dome – similar shape.
- A volcano where magma reaches the surface through a vent or a pipe.
- A volcano whose eruption buried and destroyed two Roman towns.
- An instrument used for recording all the world tremors and earthquakes.
- The surface position immediately higher up the origin of an earthquake.
- The region where there are highest number of geysers and hot springs.
Reply:
- Horst
- Crater
- Basic-Lava
- Dormant Volcano
- Acid-Lava Dome
- Fundamental blazon volcano
- Vesuvius
- Seismograph
- Epicentre
- Yellowish rock park (UsA.)
Question 27.
(a) Which blazon of lavas weather into more fertile soil. Proper name besides i useful feature of volcanicity other than soil fertility.
(b) Which four of the post-obit words are connected with volcanic activity : Karst, crater, drumlin, stalactite, gully, potholesl, ash, basalt, swallow, holes, dyke, domes, bluffs.
Answer:
(a) Basic – blazon lava canvas atmospheric condition into fertile soil eastward.yard.Deccan trap soil. Other useful feature of volcanicity is that the precious minerals come out with the magma near the land surface e.m. diamond and gold etc.
(b) Crater, ash, dyke, domes.
Question 28.
What are tectonic movements ? How are these classified?
Answer:
Tectonic movements are changes through earth's natural activities which are known as 'diastrophism'. These movements are of two types e.g. vertical movement and horizontal motion.
Question 29.
Give reasons for the following :
- Earth movements have modified the World's surface.
- Internal processes are different from external processes.
- Folding and faulting oft become together.
- World as a whole does not expand.
Answer:
- Earth movements like Continental Drift theory changed the whole confront of the earth into distinct continents and oceans of today with highest mountains plateaus plains drainage organization and then on.
- Internal processes are associated with tectonic forces resulting in drastic changes e.g. earthquakes volcanoes etc. External processes are carried on past natural agents of change e.g. h2o air current and ice which produce gradual changes.
- Folding and Faulting frequently go together because the stress on folding exceeds more plenty then folds intermission through error line to two pieces slipping one upon another which is called faulting.
- Inspite of various changes occurring within the globe information technology does not expand as it is affected by the centripital force of gravity working towards the centre of the earth.
Question 30.
How the theory of plate tectonics has explained the formation of mountains similar Himalaya or Alps and of the volcanic islands.
Answer:
The germination of the highest mountains of Himalayas and Alps have been created by the bucking up of the geo synclines of tethys sea between Angaraland and Gondwanaland which pushed towards each other and forced the geosynclines to be lifted up forming the mountains. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is the proof of the edge raised at the articulation of continental plates which gives birth to several volcanic islands.
Question 31.
(a) Draw the distribution of volcanoes in the world.
OR
Name the important belts of volcanoes.
(b) What are the influences of volcanoes eruption on homo?
OR
What is the importance of volcanoes ?
OR
Mention agin and beneficial furnishings of volcanoes.
Answer:
(a) Obviously volcanoes will be found in those regions where the chaff of the world is weak because lava can hands be discharged from such places. These are found in areas of Fold mountains. At that place are iii principal belts of volcanoes :
- Circum-Pacific Belt : This chugalug runs round the Pacific Ocean in Asia and the America. It starts from Cape Horn goes along the Andes and the Rockies to Alaska. From their information technology turns westwards and passing through Aleutian Islands Japan and Formosa goes to the Philippine Island. Here one branch goes to East Indies that is Java Sumatra and Bameo and other branch goes to New-Zealand. Some of the well known Volcanoes are Karakatoa (on a hilly island between Sumatra and Coffee) Mayon (Due north. Philippines) Fujiyama (Japan) Chimborezo and Cotopaxi (Equador S. America).
- Mid World Mountain Belts : This belt starts from the West Indies and passing through the Canavy Islands. The Mediterranean bounding main Caucasus mountains and Turkey reaches the Himalayas. Mt. Vesuvius (Italy) Mt Stromboli (Sicily) Etna (the Mediterranean sea) and Mt. Pelee (Due west Indies) are the important Volcanoes of this belt.
- African Belts : This chugalug follows the Peachy African Rift Valley. This chugalug running through Red Sea extends upto Africa. Important Volcanoes are Kilimanjaro Republic of kenya Canary Islands St. Helena (Atlantic body of water).
(b) Adverse effects of volcanoes
- Most of the recently formed volcanic areas are barren and forbidding to human.
- The sudden flow of basic lava from an eruptive volcano may cause the full destruction of man life property and crops in the neighbouring areas.
- The Karakatoa volcanic eruption (in 1883) caused such high sea waves that Karakatoa and several other neighbouring islands were completely destroyed.
- Volcanoes eruption of Vesuvius in 79 A.D. buried and destroyed completely the ii Roman towns of Pompeii and Herculaneum.
Beneficial effects of Volcanoes :
- The soil made up of lava is very fertile.
- Lakes are formed when the craters are filled upwardly with waters.
- Several minerals which are institute deep down come up upward nigh the surface of the globe.
- Lava flows take preserved many fossils which throw much light on the by life.
Question 32.
What are the post-obit :
(a) Fissure blazon of volcanoes
(b) Spine or plug
(c) Caldera
(d) Mud volcanoes
(due east) Epicentre
(f) 'Ring of Fire'
(one thousand) Cinder Cone
Answer:
(a) Fissure type of volcanoes : A volcano is a vent in the earth's crust out of which hot molten rocks (lava) menstruation. The hot rocks may as well eject violently in the grade of solid pieces. If the vent is in the class of a long crack then it is knows every bit a Fissure Type Volcano. In this type volcanic activity occurs quietly the lava upwells silently and spreads over a large area giving ascent to volcanic plateaux and extensive lava sheets.
(b) Spine or plug : Acid lava dome is formed when viscous lava solidifies apace and gives rise to steep sloping cones. This is known as a spine or plug. Sometimes these spines and plugs are exposed by denudation.
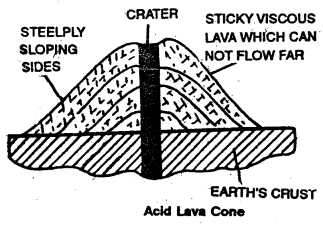
(c) Caldera : In some volcanoes the summit of the volcano blows upwards during a violent explosion resulting in the formation of a large depression called a Caldera. Some calderas may take been formed past the collapse of the pinnacle portion. Calderas are occupied by large lakes. The lake in the caldera is called the crater lake. In the state of Oregon in the United States there is a caldera which is about ix km in bore.
(d) Mud volcanoes : If water which erupts in a volcano is muddy then a conical mound of mud is formed within a creater at the elevation. This is known as a mud volcano. Such mud volcanoes are found in New Zealand Sicily and other areas of volcanic activity.
(e) Epicentre : The point on the world's surface directly above the 'focus' of convulsion is chosen epicentre.
(f) Ring of Fire ; The Circum-Pacific Belt of volcanoes encircles the Pacific Ocean in Asia and the Americas along the weak coastal chaff. It is called the 'Ring of Fire' because at that place are a large number of active volcanoes in it. The belt begins from the volcanic islands of Southward America and includes the Andes mountains of the Primal America and Mexico the western part of the Rockies in the UsaA. Canada and Alaska.
(g) Cinder cone : When the lava is ejected from a central vent its pieces and fragments solidify round the vent to form a cone. This is known as a Cinder Cone.
Question 33.
Distinguish between the post-obit pairs of terms associated with vulcaniaty
- Magma and Lava
- Acidic Lava and Bones lava
- Cinder Cone and Composite Cone
- Fissure-type Volcanoes and Primal Blazon Volcanoes
- Crater and Caldera
- Laccolith and Lapolith
- Geysers and Hot springs
- Active Volcano and Fallow Volcano
- Folding and Faulting
- Volcanic Cone and Volcanic Plateau
- Seismic Focus and Epicentre
- Dykes and Sills
(b) Distinguish between the following pair of terms associated with crustal motility of the Earth
- Graben and Horst
- Tilted Block Mountains and Listed Block Mountains
Respond:
(i) Magma and Lava :
Magma :
- Magma is hot sticky molten material.
- It contains solutions of water and gases.
- It comes out during volcanic eruptions.
Lava :
- Lava is solidified magma.
- Gases and water disappear after evaporataion.
- Information technology cools downwardly equally information technology comes into contact with temper.
(ii) Acidic Lava and Bones lava
Acidic Lava :
- Information technology is highly viscous lava.
- It is light coloured like granite.
- It has low density.
- It has a high percentage of silica.
- Information technology flows slowly and results in steepsided cones or lava domes.
Bones Lava :
- It is highly fine and thin.
- It is dark coloured like Basalt.
- It has loftier density.
- It is poor in silica.
- It flows chop-chop as thin sheets resulting in shield cones.
(iii) Cinder Cone : Volcanic cones are called Cinder cones when the cloth erupted consists of cinder and other solid particles. These cones have steep slopes because they consist of particles of large size.
Blended Cone : The volcanoes which start as cinder cone and grown into large volcanic hills with alternating layers of lava and ash are called Composite cones. These cones are formed due to an explosive eruption followed by eruption of lava. Explosive eruption leads to the formation of a layer of ash while lava solidifies as a sheet on the layer of ash. This is followed by a tranquility menstruation and and then the process gets repeated.
(four) Scissure type of volcanoes : A volcano is a vent in the earth's crust out of which hot molten rocks (lava) flow. The hot rocks may also eject violently in the form of solid pieces. If the vent is in the course of a long fissure and so it is known as a Fissure Type Volcano. In this type volcanic activity occurs quietly the lava upwells silently and spreads over a large area giving rise to volcanic plateaux and extensive lava sheets.
Central-type Volcanoes : If the vent in the globe'due south crust is of such type that the rock materials come out and mounds hills or cones are formed than the volcanoes formed are known every bit Volcanoes of the Central blazon. Vesuvius and Fuji Yama are the best examples of this type.
(5) Crater and Caldera : Crater forms the summit and Caldera the enlarged mouth or the sunken crater at the heart of a volcano. When water accumulates in a crater information technology forms a crater lake and in a caldera a lake like Taba lake of Sumatra. A crater is formed as a result of overflow of lava and calera as a result of subsidence.
(vi) Laccoliths : Laccoliths are big lens-shaped intrusions which presume a dome shape. They vary in thickness and extent. When laccoliths are exposed on the surface they form depression hills.
Lapoliths : Lapoliths are saucer-shaped intrusive layer of solidified magma and sinks as shallow basins in rock-beds.
(seven) Hot Springs :
- Information technology is a stream of hot water issuing from the ground. The hot water flows unobstructed quietly and continuously.
- Hot springs are common where joints fissures and porous beds allow the free exit of h2o to the surface. The h2o becomes hot when it comes into contact with the heated rocks or upper heated steam lying deep into the earth'south crust.
Geysers :
- It is a hot spring which at regular or irregular intervals throws a jet of hot water and steam into the air.
- In the case of geyser the fissure or vent connecting the source of hot h2o to the surface is very narrow which profoundly increases the force per unit area and temperature of the hot water and then when water comes out information technology rise high into the air.
Question 34.
Give reasons for the following :
- The Belts of volcanic action and earthquakes are roughly the same.
- Basic lava cones are broader than the Acid lava cones.
- The Circum-Pacific Belt of volcanoes is called 'The Ring of Fire'.
Respond:
- The belts of volcanic activity and earthquakes are roughly the aforementioned because the movement of magma beneath the Earth is the chief cause of earthquakes and volcanoes.
- Basic lava cones are broader than the Acid lava cones because bones lava is very fluid and flows easily for a great distance earlier it solidifies where as acid lava is highly mucilaginous and flows just for a curt distance.
- The Circum-Pacific belt of volcanoes is called "The Ring of Fire" because in that location are large number of burn down volcanoes in information technology.
Question 35.
(a) Name ane useful feature of vulcanicity other than soil fertility.
(b) Out of the following words write downward the four that are connected with volcanic activity.
Karst, crater, drumlin, stalacities, gully, pot holes, ash, basalt, consume holes, dyke, domes, bluffs.
Answer:
(a) The molten rocks of vulcanicity is of considerable ecology significance other than soil fertility since it is the directly or indirect crusade of several classes of landforms. Bones lava atmospheric condition into more fertile soils.
(b) Crater, ash, basalt, dyke are connected with volcanic activity.
Question 36.
Give reasons for the following :
- Earth'south movements take modified the Earth'due south surface.
- World as a whole does not aggrandize.
Answer:
- The surface of the earth is undergoing constant alter. Some of these changes take identify all of a sudden as in the case of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes but nigh of them are gradual and tedious. Due to these changes the sediments which were originally deposited in horizontal layers are found tilted bent cleaved and twisted. In certain regions the structures which were once at sea-level in the Baltic Sea are now well above the water. Recently information technology has been found that the larger part of the coast of Scandinavia is ascension relative to bounding main-level only that of the Southern extremity is sinking. Along some coasts submerged forests and various man structures show that the land has non only risen merely at places it has too submerged. All this has happened or is happening due to the World's movements. Thus we find that the Globe's movements have modified the Earth's surface.
- Near 6 of import Convection Current Cells with over-riding six big plates have been identified below the Lithosphere. The Mid-Oceanic ridges from edges of the plates. For case the Mid-Atlantic ridge is such a ridge. The molten matter from below adds new chaff along such' ridges. Taking the world as a whole information technology has resulted in the spreading of the sea flooring at the rate of 1 cm to about 10 cm every year. Information technology is called the effective plate movement. At the aforementioned fourth dimension the crust at the other edges of the plates in oceanic trenches gets destroyed. It is called the destructive plate motility Consequently a remainder exists and the Earth every bit a whole does non expand.
Question 37.
Answer the post-obit :
- Some volcanoes erupt explosively
- Some volcanoes develop parasitic cones.
- Hot springs are common in volcanic regions.
- Earthquakes are common in the belt of young fold mountains.
- Plate margins are zones of great volcanic activity.
- Volcanic eruption is one of the main causes of earthquakes.
- The vent of a volcano when blocked results in explosive eruption.
Answer:
- Some Volcanoes erupt explosively considering the vent of a volcano.may be blocked by some sticky fabric or rock which causes the explosion.
- Some volcanoes develop parasitic cones because the chief vent grows likewise loftier and develops a parasite or a branch l cone.
- Hot springs are common in volcanic regions because undergound water gets heated by contact with hot magma.
- Earthquakes are mutual in the belt of young fold mountains because these mountains are in a state of constant flux.
- Plate margins are zones of great volcanic activity because collisions of plate margins produce the magma and allow information technology to escape through a vent, a fissure or a crevice.
- Volcanic eruption is one of the chief causes of earthquakes bacause volcanic earthquakes are acquired past gas explosions. Such earthquakes occur either simultaneously with eruption or more commonly in the flow preceding an eruption.
- It causes the pressure to build upwardly which results in tearing explosion.
copelandwittleasto.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.aplustopper.com/icse-solutions-for-class-9-geography-volcanoes/
0 Response to "what name is given to the crater at the top of a volcano caused by its collapse"
Enviar um comentário